History
The AVRO 504, a trainer, first flew in 1913. It was a development of the AVRO 500, equipped with a Gnome Monosoupape rotating engine rated 80 hp.
Several examples were obtained by the RFC and the RNAS just before the war.
The first aircraft shot happens to be an AVRO 504.
The RNAS used four aircraft to bomb the Zeppelin factories at Friedrichshafen.
As the AVRO 504 was not suited for front service, the type was used in large numbers as trainers with the designation AVRO 504J and 504K.
They were equipped with different engines, depending largely upon availability of the engine. At the end of the war over 8900 examples were built.
During the winter 1917/1918 several AVRO 504J/Ks were converted to a single seat aircraft and used by the Home Defence.
These fighters were equipped with one Lewis machine gun mounted on the upper wing and with an 100 hp Gnome or Le-Rhone engine.
About 270 aircraft were converted, at the end of the war about 220 aircraft were remaining.
After the war the type was used by the RAF for quit a long period as standard trainer. Large numbers surplus aircraft were sold for both civil as military use.
In 1925 an improved version was released, equipped with an Armstrong-Siddeley Lynx radial engine, designated AVRO 504N. 592 aircraft were built of this type between 1925 and 1932. In 1933 is was succeeded by the AVRO Tudor.
Versions
- AVRO 504:
- The original design with one Gnome engine rated 80 hp.
- AVRO 504A:
- Improved version with smaller ailerons and broader styles and one Gnome engine rated 80 hp.
- AVRO504B:
- Version for the RNAS with enlarged met larger fins and one Gnome or LeRhone engine rated 80 hp.
- AVRO 504C:
- A single seat fighter for the RNAS, used for anti-zeppelin purposes. It was equipped with an extra fuel tank.
- AVRO 504D:
- A single seat anti-zeppelin aircraft for the RFC.
- AVRO 504E:
- Version with one Gnome engine rated 100 hp.
- AVRO 504F:
- Test aircraft equipped with a Rolls Royce Hawk engine rated 75 hp.
- AVRO 504G:
- Version with a Gnome engine rated 80 hp.
- AVRO 504H:
- Version used for catapult tests.
- AVRO 504J:
- Trainer equipped with a Gnome rated 100 hp or LeRhone rated 80 hp.
- AVRO 504K:
- Trainer equipped with several types of engines. A single seat version was used to fight Zeppelins.
- AVRO 504K Mk.II: A mix of a 504K fuselage with the undercarriage and wings of the AVRO 504N.
- Yokosuka K1Y: Two seat trainer of the AVRO 504K, built for the Japanese Navy.
- U-1 (Uchebnyi - 1) Avrushka: Russian copy of the 504K, over 700 built..
- MU-1 (Morskoy Uchebnyi - 1): Russian version with floats.
- AVRO 504L:
- Float version with a Bentley BR1, rated 150 hp or Clerget rated 130 hp or a Le-Rhone rated 110 hp.
- AVRO 504M:
- Version with a cabin, suited to carry three passengers. Just one built.
- AVRO 504N:
- Redesigned postwar trainer for the RAF, equipped with one Armstrong Siddely Lynx rated 160 hp.
- Yokosuka K2Y1: Japanese version of the 504N, equipped with a Mitsubnishi built Armstrong-Siddeley Mongoose rated 130 hp.
- Yokosuka K2Y2: Improved version of the K2Y1, equipped with one Gasuden Jimpu 2 engine rated 160 hp.
- AVRO 504O:
- Float version of the 504N.
- AVRO 504P:
- Never built version of the 504N with seats side by side.
- AVRO 504Q:
- Three seat version, especially built for the Oxford University Arctic Expedition, equipped with an Armstrong Siddeley Lynx engine.
- AVRO 504R Gosport:
- Revised trainer with a light weigth structure. Five protoypes flew between 1926 en 1927 with different engines. In the end the Armstrong Siddeley Mongoose rated 150 hp was selected for production.
- AVRO 504S:
- Two seat trainer, built in Japan by Nakajima.
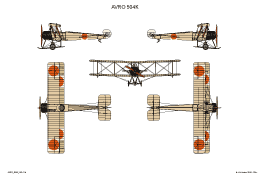
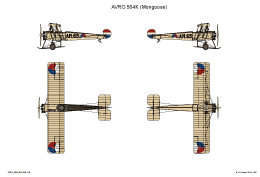
AVRO 504
This is the original version developed in 1913.
| Dimensions: | |||
| Length: | 8,97 m | Wingspan: | 10,97 m |
| Height: | 3,17 m | Wing area: | 30,7 m2 |
| Weights: | |||
| Empty weight: | 558 kg | Max. Start weight: | 830 kg |
| Performance: | |||
| Max. Speed: | 145 km/hr | Climbing speed: | 5 minutes to 3500 m |
| Cruising speed: | 126 km/hr | ||
| Range: | 402 km | Service ceiling | 4875 m |
| Miscellaneous: | |||
| Engine Type: | One Gnôme rated 80 pk | ||
| Crew: | Two men | ||
| Armament: | . | ||
AVRO 504A
A modified version with smaller ailerons and more broad struts; equipped with one Gnôme engine rated 80 pk.
| Dimensions: | |||
| Length: | 8,97 m | Wingspan: | 10,97 m |
| Height: | 3,17 m | Wing area: | 30,7 m2 |
| Weights: | |||
| Empty weight: | 558 kg | Max. Start weight: | 830kg |
| Performance: | |||
| Max. Speed: | 145 km/hr | Climbing speed: | 5 minutes to 3500 m |
| Cruising speed: | 126 km/hr | ||
| Range: | 402 km | Service ceiling | 4875 m |
| Miscellaneous: | |||
| Engine Type: | One Le Rhône 9C rated 80 pk | ||
| Crew: | Two men | ||
| Armament: | . | ||
AVRO 504B
Version of the AVRO 504 developed on behalf of the RNAS, with a larger fin and a Gnôme or Le Rhône engine rated 80 hp.
| Dimensions: | |||
| Length: | 8,97 m | Wingspan: | 10,97 m |
| Height: | 3,17 m | Wing area: | 30,7 m2 |
| Weights: | |||
| Empty weight: | 558 kg | Max. Start weight: | 830kg |
| Performance: | |||
| Max. Speed: | 145 km/hr | Climbing speed: | 5 minutes to 3500 m |
| Cruising speed: | 126 km/hr | ||
| Range: | 402 km | Service ceiling | 4875 m |
| Miscellaneous: | |||
| Engine Type: | One Gnôme rated 80 pk | ||
| Crew: | Two men | ||
| Armament: | . | ||
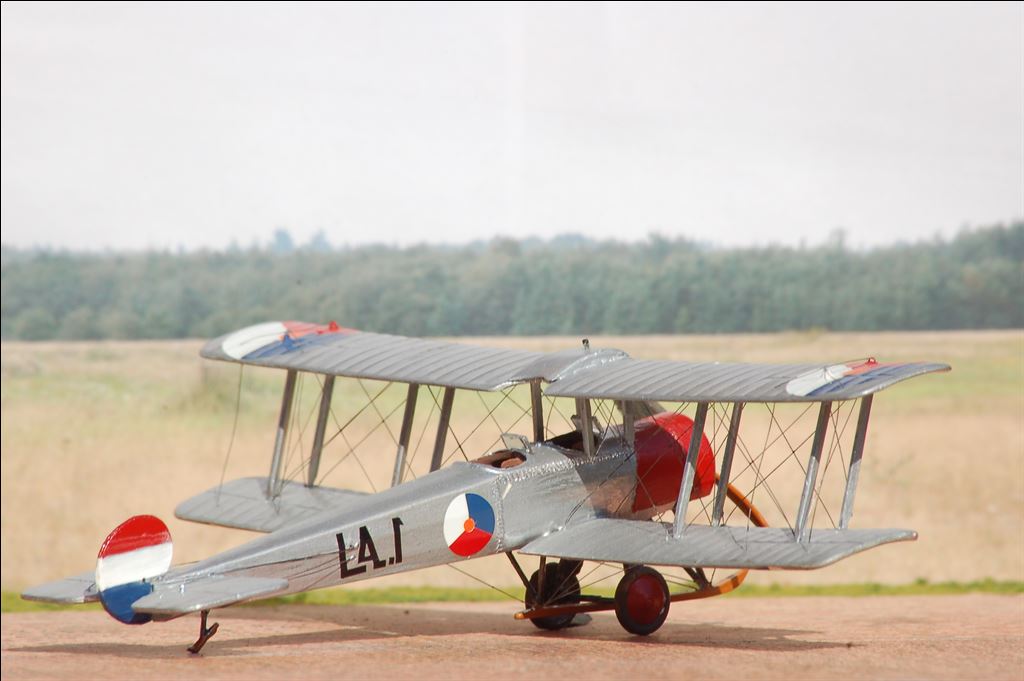
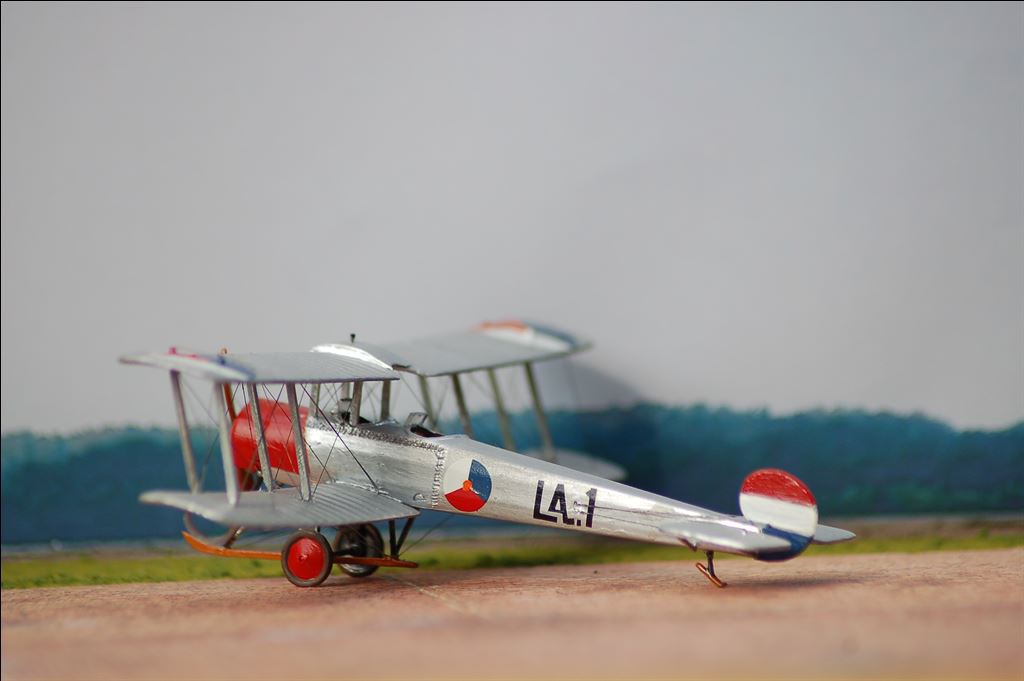
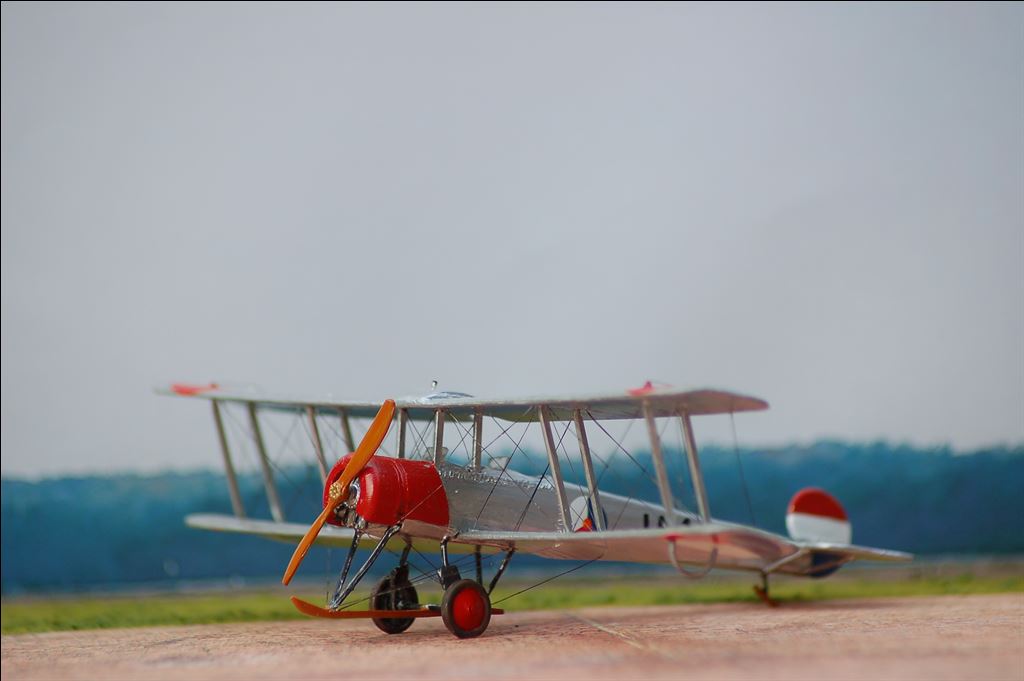
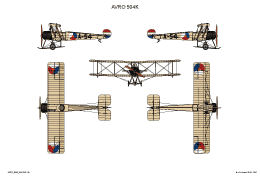
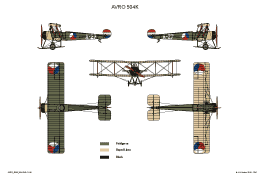
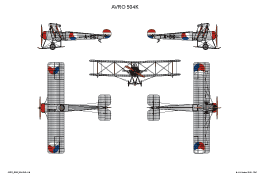
AVRO 504K
This was a two seat trainer. It was used with a wide range of different engines. Most used were the Clerget rated 130 hp; Gnome rated 100 pk or Le Rhône rated 110 hp.
| Dimensions: | |||
| Length: | 8,97 m | Wingspan: | 10,97 m |
| Height: | 3,17 m | Wing area: | 30,7 m2 |
| Weights: | |||
| Empty weight: | 558 kg | Max. start weight: | 830 kg |
| Performances: | |||
| Max. speed: | 145 km/hr | Rate of climb: | 5 minutes to 3500 m |
| Cruising speed: | 126 km/hr | ||
| Range: | 402 km | Service ceiling: | 4875 m |
| Miscellaneous: | |||
| Engine type: | One Le Rhône 9C rated 80 hp. | ||
| Crew: | Two men | ||
| Armament: | None | ||
In service with LVA and NEIAF.
In service with LVA.
The first AVRO 504A, no RFC 733, landed on March 21, 1915 at St Kruis in Zeeland and was interned as LA-13.
The engine of this aircraft, one of 80 hp Gnome, was replaced in 1917 by a Thulin engine.
In 1918 the serial was changed to A-21. Later, when the aircraft was only used for ground training, the serial was changed in A-1.
The second AVRO, an AVRO 504B with serial number 1001 from RNAS, landed on March 24, 1915 near Kruiningen. This AVRO was also interned and registered with serial LA14.
Of this aircraft the engine was also replaced with a Thulin engine. In 1918 the serial was changed to A-22. Both aircraft were written off in 1919.

[Enclosed photo from BeeldBank NIMH. Click on photo for ordering information]

[Enclosed photo from BeeldBank NIMH. Click on photo for ordering information]

[Enclosed photo from BeeldBank NIMH. Click on photo for ordering information]
In service with NEIAF.
Just after the First World War the Dutch East Indies bought several airplanes to set up the new Flight Division of the NEI Army. Besides a number of Airco DH-9s, a number AVRO 504Ks was bought.
The first two Avro 504 arrived in August 1919. In 1922, another twelve aircraft were delivered.
The AVRO 504K was used as training aircraft. Despite a number of accidents, the aircraft did very well.
In 1924 a start was made to built an improved version of the AVRO 504K, initially at Andir, later at Soekamiskin. These AL aircraft had a plywood fuselage and improved fuel tank. The prototype was the LA-1 (later serialled as AL-57).
Late twenties and early thirties was a replacement was necessary and one Fokker S. IV and one Morane-Saulnier AR-35-EP-2 were bought. The AVRO turned out to be at least as good as these both types. So most remaining units were given a facelift in 1931; an Armstrong Siddeley Mongoose engine was built in to replace the Clerget rotary engine. These were re-serialled "AM" with the original aircraftnumber. In 1938, the last Avro 504K went out of service.

[Enclosed photo from BeeldBank NIMH. Click on photo for ordering information]

[Enclosed photo from BeeldBank NIMH. Click on photo for ordering information]

[Enclosed photo from BeeldBank NIMH. Click on photo for ordering information]

[Enclosed photo from BeeldBank NIMH. Click on photo for ordering information]

[Enclosed photo from BeeldBank NIMH. Click on photo for ordering information]
Serial overview LVA and NEIAF.
Serial overview LVA
| Serial | Constr. nr. | RFC-serial | Date in service | Date out of service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LA13 | 753 | 21-03-1915 | AVRO 504A | ||
| LA14 | 1001 | 24-03-1915 | AVRO 504B |
Serial overview NEIAF
AVRO 504K (ex RFC)
| Serial
Serial
|
Constr. nr.
Constr. nr.
|
Date in service
Date in service
|
Date out of service
Date out of service
|
Notes
Notes
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bought in may 1919 | ||||
| A-22 | ||||
| A-23 | ||||
| A-24 | ||||
| A-25 | ||||
| A-26 | ||||
| A-27 | ||||
| A-28 | ||||
| A-29 | ||||
| A-30 | ||||
| A-31 | ||||
| A-32 | ||||
| A-33 | ||||
| A-34 | ||||
| A-35 | ||||
| A-36 | ||||
| A-37 | ||||
| Bought in December 1919 | ||||
| A-38 | ||||
| A-39 | ||||
| A-40 | ||||
| A-41 | ||||
| A-42 | ||||
| A-43 | ||||
| A-44 | ||||
| A-45 | ||||
| A-46 | ||||
| A-47 | ||||
| A-48 | ||||
| A-49 | ||||
| Bought in November 1922 | ||||
| A-50 | ||||
| A-51 | ||||
| A-52 | ||||
| A-53 | ||||
| A-54 | ||||
| A-55 | ||||
| A-56 | ||||
AVRO 504K (home built)
| Serial
Serial
|
Constr. nr.
Constr. nr.
|
Date in service
Date in service
|
Date out of service
Date out of service
|
Notes
Notes
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AL-57 | ||||
| AL-58 | ||||
| AL-59 | ||||
| AL-60 | ||||
| AL-61 | ||||
| AL-62 | ||||
| AL-63 | ||||
| AL-64 | ||||
| AL-65 | ||||
| AL-66 | ||||
| AL-67 | ||||
| AL-68 | ||||
| AL-69 | ||||
| AL-70 | ||||
| AL-71 | ||||
| AL-72 | ||||
| AL-73 |
1/72nd Scale
Kits
- HR Models
- Kit 7208: A model of the AVRO 504A
- Kit 7203: A model of the AVRO 504B
- A Model
- Kit 7259: A model of the AVRO 504K
- Kit 7253: A model of the Petrograd U1 (licence built AVRO 504K)
- Kit 72246: A model of the AVRO 504K/U1
- Airfix
- Kit 01085: A model of the AVRO 504K
Modelling add-on
- Aeroclub
- Set P053: Wooden 4 Bladed Prop (DH4)
- Part Etchings
- Set S72-166: detailling set
Decals
- --
- Set --: --
1/48th Scale
Kits
- Blue Max
- Kit 206: AVRO 504K (spuitgiet kit)
Modelling add-on
- --
- Set --: --
Decals
- --
- Set --: --
| Scheme | Colour name | FS-number | Humbrol | XtraColor | Vallejo Model Color | Vallejo Model Air | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard #1 National insigna orange balls and black serials. |
Whole aircraft | PC12 | ~3531 | 121 | X105 | ||
| Upper sides | Fieldgreen | ~4102 | 117 | X116 | |||
| Fieldbrown | ~0117 | 186 | |||||
| Metal parts | Black | ~7038 | 21 | ||||
| Wooden parts | Varnish | ||||||
| Scheme | Colour name | FS number | Humbrol | XtraColor | Vallejo Model Color | Vallejo Model Air | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard #1 | Whole aircraft | PC12 | ~3531 | 121 | X105 | ||
| Upper sides | Fieldgreen | ~4102 | 117 | X116 | |||
| Fieldbrown | ~0117 | 186 | |||||
| Engine cowling and metal parts | Zwart | ~7038 | 21 | ||||
| Wooden parts | Varnish | ||||||
| NEIAF before 1926: aircraft A-26 - A-52 | |||||||
| Standard #2 | Whole aircraft | Khaki | ~4086 | 108 | X144 | ||
| Linen horizontal parts | Doped Linen | ~3531 | 121 | X105 | |||
| Some aircraft e.g. A-42, A-43 | |||||||
| Standard #3 | Overall | NIVO green | ~4096 | Mix: 6*116 + 6*177 + 1*163 (105) | X211 | ||
| NEIAF after 1926: Aircraft A-26 - A-52 | |||||||
| Standard #4 | Overall | Aluminum dope | ~7178 | 191 | X216 | ||
| Landing gear | Black | ~7038 | 21 | ||||
| Engine cowl and wheel covers | Red | 19 | |||||
| NEIAF: Home built 405K: serials A-57 - A-73 | |||||||
| Standard #3 | Whole aircraft | Aluminum dope | ~7178 | 191 | X216 | ||
Check www.paint4models.com for an extensive conversion table with lots of colour and paint systems.
Literature.
| Van Brik tot Starfighter | H. Hooftman | 1965 | La Rivière en Voorhoeve - Zwolle | |
| Nederlandse Militaire Luchtvaart in Beeld, deel 1. | Hugo Hooftman | pag. 14 - 15 | 1977 | Europese Bibliotheek, Zaltbommel |
| KLu Vliegtuigen | W. Schoenmaker/Th.Postma | Pag. 21 - 22 | 1987 | Uitgave: De Alk Alkmaar |
| Camouflage en Kentekens | J.Greuter e.a. | 1997 | Bonneville – Bergen (NH) | |
| Air Enthusiast no.80, The Historical Aviation Journal: Unexpected Windfalls | Bart van der Klaauw | Pag. 54 - 59 | 1999 | Key Publishing, Stamford |
Websites.













 Nederlands (nl-NL)
Nederlands (nl-NL)  English (United Kingdom)
English (United Kingdom)